From D to Z: Master the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart Before You Buy
Understanding a diamond’s beauty begins with more than just its sparkle — it lies in the subtle details revealed by the diamond color and clarity chart. These two factors, the color and clarity of diamond, determine how pure, bright, and valuable each stone truly is. In this diamond guide, we’ll explore how to interpret these grades, what they mean for your purchase, and how they impact both appearance and price, helping you make an informed choice before you buy a diamond ring or other diamond jewelry.
What is the Color of the Diamond?
The diamond color refers to the depth of hue visible within a diamond’s transparency, primarily assessing whether it carries yellow or brown tones. The color of a diamond directly affects both its appearance and overall value. Among all diamond color ratings, colorless diamonds are often seen as the symbol of the best diamond clarity, as they allow light to pass and reflect freely, creating a brighter and purer brilliance. In general, the cleaner the diamond’s color, the higher its overall worth.
Understanding the Diamond Color Scale
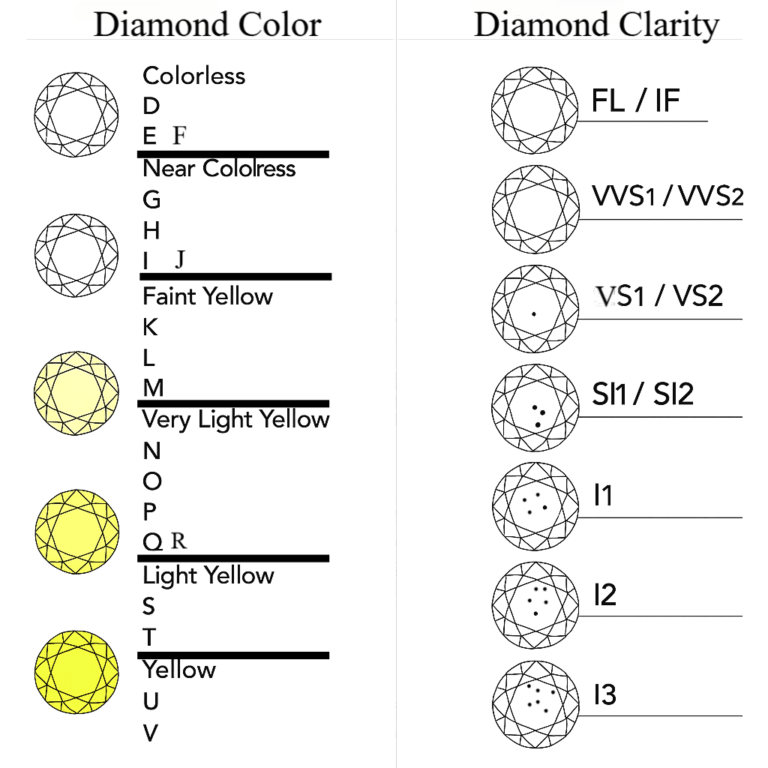
The diamond color grading system comes from an internationally recognized standard, primarily established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). This system uses letters D–Z to scientifically assess the depth of diamond color in diamonds of different colors, ensuring that each diamond’s color grade is clear and reliable. Read the diamond color explained below to fully understand the color scale for diamonds.
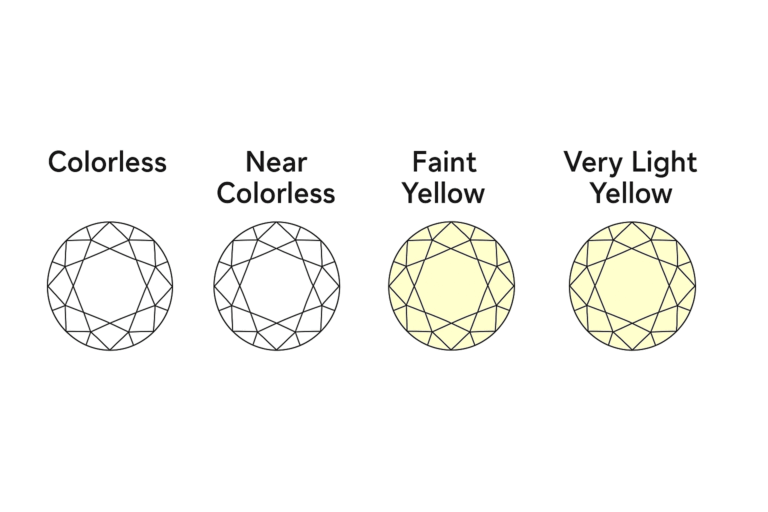
Colorless Diamond Scale Grades
D Color Grade Diamonds
The D color diamond represents the highest clarity of a diamond among diamond color grading scale and is considered the best color of diamonds, often referred to as the ideal diamond color. It is the rarest and most valuable grade among all. A D color diamond is completely colorless, showing virtually no traces of yellow or brown tones. Its pure transparency allows maximum light reflection and refraction, resulting in exceptional brilliance and fire.
E Color Grade Diamonds
An E color diamond shows virtually no visible color to the naked eye, though a faint tint may be detected under professional examination. It is just as rare as a D color diamond but is slightly more affordable in price.
F Color Grade Diamonds
An F color diamond is still classified as a colorless diamond, with only a slight tint visible under professional equipment. To the naked eye, it appears virtually identical to higher grades. Like D and E color diamonds, it offers exceptional brilliance and fire, making it ideal for everyday wear or as an engagement ring. Its price is slightly lower than D and E grades, offering excellent value for its quality.

Near Colorless Diamond Scale Grades
G Color Grade Diamonds
A G color diamond is the highest grade within the near colorless range. Its color is extremely faint and can only be noticed when compared directly with higher-grade diamonds. It still appears bright and clear to the eye, showing minimal difference from D–F grades, making it one of the most high-quality and cost-effective choices available.
H Color Grade Diamonds
An H color diamond appears colorless under most lighting conditions, with only a slight warm tint visible under strong light or professional inspection. This color grade offers an excellent balance of brightness and affordability, making it a popular choice for engagement rings and everyday wear.
I Color Grade Diamonds
An I color diamond shows a slightly more noticeable yellow tint than an H color diamond, but it still appears natural and subtle to the naked eye. When set in rose gold or yellow gold, its hue blends beautifully with the metal, giving the diamond a warm and elegant appearance.
J Color Grade Diamonds
A J color diamond leans toward a light yellow tone that can be seen against a white background. However, it still maintains impressive brilliance and sparkle, making it an excellent option for buyers who want a larger diamond at a more affordable price.
Faint Color Diamond Scale Grades
K Color Grade Diamonds
A K color diamond shows a subtle yellow tint that is more noticeable against a white background. However, when set in yellow gold or rose gold, the hue is gently softened, giving the diamond a warm and elegant appearance. It is a popular choice for buyers seeking a balance between carat size and budget.
L Color Grade Diamonds
An L color diamond has a more noticeable yellow tint than K grade but still reflects good brightness and fire. It is suitable for buyers looking for larger diamonds who don’t mind a slight color presence. When set in warm-colored metals, the diamond maintains an appealing visual effect.
M Color Grade Diamonds
An M color diamond has a more obvious yellow tint that is easily visible to the naked eye when viewed as a loose stone, yet it still retains sparkle and brilliance. When paired with vintage or warm-toned settings, it can create a unique classic look. This grade is often used in personalized designs or vintage-style jewelry pieces.
Very Light and Light Color Diamond Grades
Very Light and Light color diamonds show a more noticeable yellow or brown tint than faint color diamonds but still retain good brilliance and sparkle. On the GIA scale, they generally range from N–R (Very Light) to S–Z (Light Color). While the color is visible, these diamonds remain attractive and offer an affordable option for buyers prioritizing size or budget.
Factors Affecting Diamond Color Perception
Lighting Conditions
The perceived color of a diamond can change depending on the lighting. Natural daylight, incandescent bulbs, and fluorescent lighting each interact differently with a diamond’s facets, which can make subtle yellow or brown tones more or less noticeable.
Diamond Cut and Faceting
A diamond’s cut affects how light travels through it. Well-cut diamonds reflect more light and can mask minor color tints, while shallow or deep cuts may accentuate any underlying color, influencing how bright or dull the diamond appears.
Surrounding Colors
Colors near a diamond, such as the metal of the setting or other gemstones, can influence its perceived color. For example, yellow gold can make a diamond look slightly warmer, whereas white gold or platinum can enhance a cooler, whiter appearance.
Diamond Size and Shape
Larger diamonds tend to show color more easily than smaller stones because light has to travel farther through the stone. Similarly, elongated shapes like emerald cuts can reveal more color, whereas round brilliant cuts often conceal it better.
Understanding Diamond Clarity Scale
FL(Flawless) and IF(Internally Flawless) Diamond Clarity
Flawless (FL) and Internally Flawless (IF) diamonds represent the highest clarity grades. A flawless diamond has no internal or external imperfections visible under 10x magnification, while IF diamonds are free of internal flaws but may have minor surface blemishes. Both offer exceptional brilliance and rarity.
VVS1 & VVS2(Very, Very Slightly Included) Diamond Clarity
VVS1 and VVS2 diamonds are graded as Very, Very Slightly Included, with inclusions extremely difficult to detect under 10x magnification. The vvs2 clarity grade indicates minor internal flaws nearly invisible to the naked eye, reflecting the high standard of clarity in diamonds prized for brilliance and rarity.
VS1 & VS2(Very Slightly Included) Diamond Clarity
VS1 and VS2 diamonds have very slight inclusions, often invisible without magnification. A vs1 diamond represents a higher clarity, with inclusions extremely difficult to detect, while a vs2 diamond may show minor flaws under 10x magnification. Both grades offer excellent brilliance and value, making vs1 clarity highly desirable.
SI1 & SI2(Slightly Included) Diamond Clarity
SI1 and SI2 diamonds are classified as Slightly Included, meaning inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification but often invisible to the naked eye. These diamonds balance beauty and affordability, offering a sparkling appearance while being more accessible than higher clarity grades.
I1, I2 & I3(Included) Diamond Clarity
I1, I2, and I3 diamonds are classified as Included, with inclusions visible under 10x magnification and often to the naked eye. While they may have noticeable internal flaws, these diamonds can still offer brilliance and are generally more affordable, making them an option for budget-conscious buyers.
Diamond Color and Clarity Chart
Common Inclusions and How They Impact Sparkle
Typical diamond inclusions include crystals, feathers, clouds, and pinpoints. These internal features can scatter or block light, reducing a diamond’s brilliance and fire. While small inclusions often have minimal effect, larger or centrally located ones can noticeably diminish sparkle, especially in higher-clarity stones.
Also Read: The Secret Of Imperfection In A Diamond A Buyers Complete Guide
How the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart Work Together
The diamond color and clarity charts are closely linked in determining a diamond’s overall quality and value. Color measures the presence of yellow or brown tints, while clarity assesses internal and external flaws. A high-clarity diamond can appear brighter even if its color is slightly lower, whereas a top-color diamond with visible inclusions may lose sparkle. By evaluating both charts together, buyers can balance visual beauty and rarity, choosing diamonds that maximize brilliance, fire, and overall appeal within their budget.
Using the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart When Shopping Online
When shopping online, a diamond chart for color and clarity helps you compare stones without seeing them in person. Checking the color and clarity of diamonds allows you to identify high-quality options—typically D–F for color and VS1–VS2 for clarity—offering excellent brilliance and minimal visible flaws. To shop with confidence, always request a certificate verifying the diamond’s color and clarity. This ensures you know exactly what is a good color and clarity diamond before purchasing, making online buying safer and more reliable.
Expert Tips for Maximizing Visual Beauty
To maximize a diamond’s visual appeal, focus on a balanced combination of cut, color, and clarity. Well-cut diamonds reflect light more efficiently, enhancing sparkle, while higher color grades prevent unwanted tints. Choosing stones with minimal inclusions ensures brilliance isn’t blocked. Additionally, pairing the diamond with complementary settings and proper lighting can further elevate its perceived beauty, making each stone appear more vibrant and captivating.
AmandaFineJewelry offers ideal diamond jewelry for various ideas and needs. Browse Amanda’s lab diamond wedding jewelry to fine your diamond of good quality.
Conclusion: Mastering the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart
Mastering the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart empowers buyers to make informed decisions online or in-store. By understanding how color and clarity grades affect brilliance and rarity, you can identify high-quality diamonds that match your preferences and budget. Using the chart alongside certification ensures confidence in your purchase, helping you select a diamond that shines beautifully and retains value over time.
FAQs About the Diamond Color and Clarity Chart
What is the diamond color and clarity chart?
The Diamond Color and Clarity Chart is a standardized grading system developed by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) to assess the quality of diamonds based on two key factors: color and clarity. Color grades range from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown), while clarity grades range from Flawless (FL) to Included (I3). This chart helps consumers evaluate diamonds’ appearance and value.
How does diamond color affect its appearance and value?
Diamond color refers to the presence of any color in the diamond, with D being completely colorless and Z having noticeable color. Colorless diamonds (D-F) are rarer and more valuable due to their brilliance and rarity. Near-colorless diamonds (G-J) offer a balance between appearance and cost, while diamonds with noticeable color (K-Z) are less expensive but may have a warmer hue.
What does diamond clarity mean?
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal inclusions or external blemishes. The GIA clarity scale ranges from Flawless (FL) to Included (I3). Flawless diamonds have no visible inclusions or blemishes under 10x magnification, while Included diamonds have noticeable imperfections that can affect their appearance and durability.
What does diamond color mean?
Diamond color refers to the presence of any tint, usually yellow or brown, in a diamond. The less color, the higher the grade and value.
What colors can diamonds be?
Diamonds can range from colorless to light yellow or brown. Some rare diamonds also come in fancy colors like blue, pink, or green.
What colors do diamonds come in naturally?
Naturally, most diamonds are shades of yellow or brown. Truly colorless diamonds are rare, while fancy-colored diamonds occur due to trace elements or structural anomalies.
What is the best clarity and color for a diamond?
The best combination is generally D–F color and FL–VS2 clarity. This ensures minimal visible color and inclusions for maximum brilliance.
Is VS1 or VS2 clarity good?
Yes, both VS1 and VS2 diamonds are considered high quality. Inclusions are very difficult to see without magnification, and they maintain excellent sparkle.
What color and clarity is good for a diamond ring?
A diamond ring looks best with near-colorless to colorless grades (D–G) and VS1–VS2 clarity. This combination balances beauty, brilliance, and value
How do color and clarity impact a diamond's appearance?
Both color and clarity significantly influence a diamond’s brilliance and overall visual appeal. A higher color grade (D-F) ensures a more colorless and brighter appearance, while a higher clarity grade (FL-VVS2) indicates fewer imperfections, leading to greater brilliance. However, the cut quality also plays a crucial role in maximizing a diamond’s sparkle.
Should I prioritize color or clarity when choosing a diamond?
While both are important, many experts suggest prioritizing color over clarity. This is because color has a more noticeable impact on a diamond’s appearance. Choosing a diamond with a higher color grade can enhance its brilliance, even if the clarity grade is slightly lower. However, it’s essential to find a balance that fits your personal preferences and budget.
Are diamonds with higher clarity always better?
Not necessarily. While higher clarity diamonds have fewer imperfections, many inclusions are microscopic and not visible to the naked eye. Diamonds with clarity grades of VS1 or VS2 often appear flawless to the naked eye and can offer better value without compromising on appearance.



